U.S. economic data again "burst" ECB forum into hawks to meet Japan "out of place"?
On June 28, Federal Reserve Chairman Powell will attend the ECB Central Bank Forum to participate in a policy panel discussion, along with Bank of England Governor Pele, ECB President Lagarde, Bank of Japan Governor Ueda and Male.。It is worth noting that three of the four top central bank leaders mentioned above have recently expressed hawkish views。
On June 27, local time, the United States released a number of economic data, all exceeding expectations。
Strong Economic Data U.S. Stocks Close Up Across the Board Interest Rates Reversed and Narrow
On the consumer front, the U.S. Conference Board Consumer Confidence Index recorded 109 in June..7, the highest since March 2022, consumer confidence boosted by recent strong labor data。In the manufacturing sector, the monthly rate of durable goods orders in the United States recorded 1.7%, better than expected -1%, while the U.S. Richmond Fed Manufacturing Index for June was released at -7, also stronger than expected at -12 and better than all economists expected, representing a gradual expansion of U.S. manufacturing activity.。
Real estate continued its bright performance, with the U.S. FHFA house price index rising at a monthly rate of 0 in April..7%, the total number of new home sales in the United States in May reached 76.30,000, while the U.S. S & P / CS20 home price index posted an annualized rate of -1 in April..7%, significantly better than expected -2.6%。
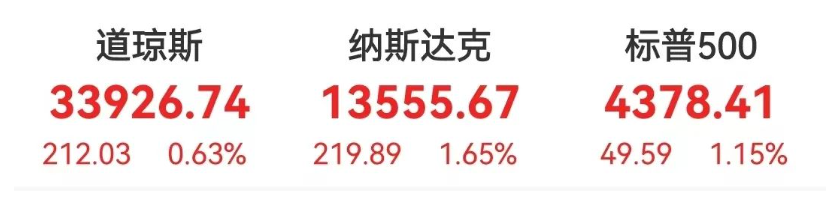
A series of beautiful data also boosted U.S. stocks, with all three indexes recording gains during the session。Among them, the Dow rose 0.6%, the S & P 500 rose 1.1%, while the Nasdaq rose 1.6%。Previously, the market had underperformed due to recent outflows from the technology sector that supported U.S. stocks。
Even the closely watched difference between U.S. 10-year and 2-year Treasury yields narrowed to a 3-month low at 99.6 basis points。The inversion of the yield curve on U.S. Treasuries is often seen as a warning of an imminent recession, and according to the recently released Markets Live Pulse (MLIV Pulse) mid-year survey, 80 percent of respondents predict that the inversion of the U.S. Treasury yield curve will continue until 2024。
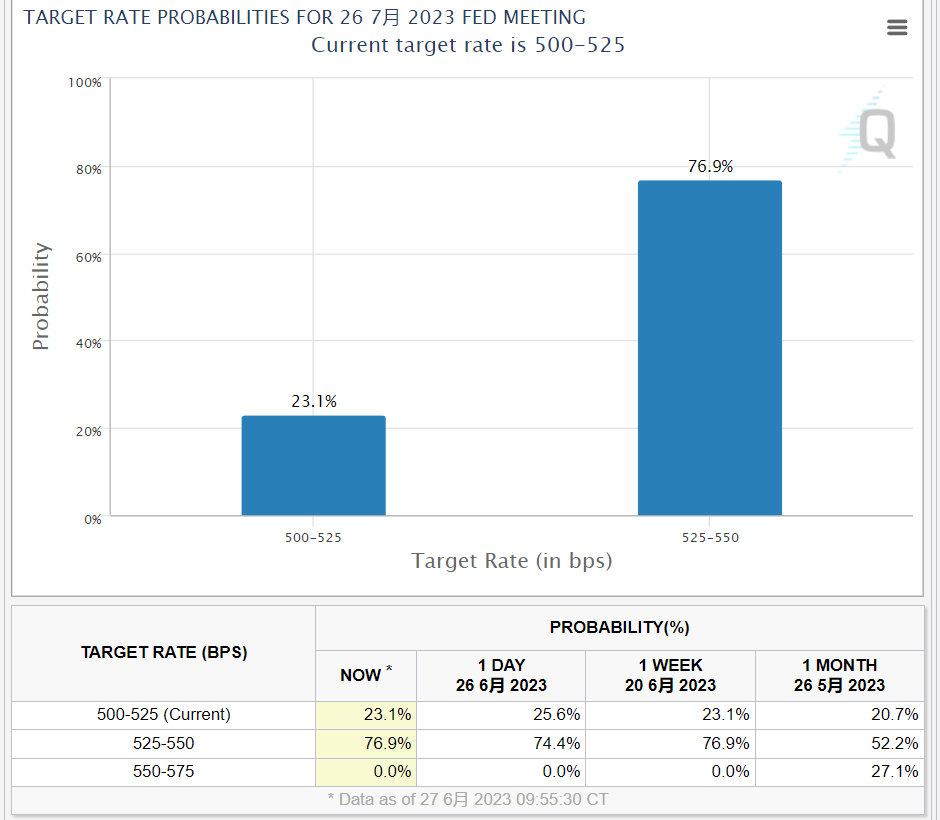
Strong data support the Fed's determination to raise interest rates in July。According to the latest CME Fed Watch data, the market priced the probability of a July rate hike to 76 from the previous day..9%, unchanged from a week ago。
Today, Federal Reserve Chairman Jerome Powell (Jerome Powell) will attend the ECB Central Bank Forum to participate in policy panel discussions, along with the Bank of England Governor Andrew Bailey (Andrew Bailey), the European Central Bank President Christine Lagarde (Christine Lagarde), the Bank of Japan Governor Kazuo Ueda (Kazuo Ueda)。It is worth noting that three of the four top central bank leaders mentioned above have recently expressed hawkish views。
Fed: Inflation governance effective and strong economic data for interest rate hike.
Spurred by fiery U.S. labor and real estate data, last week, Powell re-emphasized the need for a rate hike in the current scenario while attending hearings before the U.S. House Financial Services Committee and the Senate Banking Committee.。He said the U.S. is far from meeting its inflation target and will vote for two more rate hikes during the year if the economy performs as expected。
The judgment of raising interest rates twice is based on the latest SEP bitmap released by the Federal Reserve.。According to the dot plot resolution, the Fed's median interest rate forecast for the end of the year was sharply raised to 5.625%, which means the Fed will raise interest rates at least twice in the next four meetings of the year.。According to Morgan Stanley, Powell is "one of the people on the committee who strongly believes that interest rates should be higher."。
For now, the Fed's inflation governance has been effective。According to U.S. data released last week, overall U.S. CPI rose 4% year-on-year in May, the smallest year-on-year gain since March 2021, falling for 11 consecutive months and well below the peak reached in June of last year..1%。After the data was released, the Fed pressed the rate hike pause button to keep the policy rate cap at 5.25%。
ECB: Long-term battle against rising prices needed
ECB's governance of inflation equally tough。Public data show that the bank has raised policy rates by a total of 400 basis points over the past year, and continued monetary policy pressure has slowed the eurozone economy significantly。According to the recently released S & P Global Composite Purchasing Managers Index, economic activity in the euro zone fell to a five-month low in June, hit hard by the decline in industrial production.。In addition, growth in the euro zone's services sector has stalled in recent times, and some economists have warned of the possibility of a recession.。
On June 27, local time, Lagarde said at the European Central Bank's annual economic forum that the current inflation in the euro area has entered a new stage, high inflation may continue for some time, the euro area needs a long-term fight against rising prices.。Lagarde believes that the biggest problem facing the euro area is that the initial energy-induced short-lived inflation has penetrated into the broader economy and is likely to continue, and due to lower-than-expected productivity growth, higher labor cost pressures across European companies and upward pressure on labor wages.。

Based on market pricing of interest rates in the euro zone, the market expects the ECB to raise interest rates twice this year, by 25 basis points each, in line with the Fed.。
Bank of England: there seems to be no other way but to continue raising interest rates
For its part, the Bank of England just announced its 13th consecutive rate hike since December 2021 on the 22nd of this month, taking the benchmark interest rate from 4.5% to 5%, a direct increase of 50 basis points, and announced that further monetary tightening will be needed in the future if there is evidence that inflationary pressures persist。
Inflation governance in the UK is "hell-class"。After a long period of monetary tightening, Britain's consumer price index remained at 8 in May from a year earlier..7%, significantly higher than expected。In addition, core inflation in May not only did not decline, but from the previous month's 6..8% further to 7.1%, the highest level since 1992。
In this regard, the Bank of England in addition to continue to raise interest rates, it seems that there is no better way to find more。According to agency survey data, the Bank of England will also raise interest rates twice in the third quarter, by 25 basis points each on August 3 and September 21, with the terminal rate at 5.5%, higher than previously expected。
Bailey had said after the rate decision that the economy was better than expected, but inflation was still too high and needed to be dealt with.。If you don't raise interest rates now, it will be even worse in the future.。His decision also received political support, with Chancellor of the Exchequer Jeremy Hunt (Jeremy Hunt) saying he would support the Bank of England's policy measures after the interest rate decision was announced.。Previously, he had made it clear that even a recession would be acceptable if the inflation target could be achieved。
Bank of Japan: stick to easing is not moving.
And the other three colleagues slightly "alternative" is that since May this year, Ueda and male took office as governor of the Bank of Japan, the practical monetary policy leader has been continuing his predecessor Kuroda Higashihiko's ultra-loose monetary policy, corresponding to the Nikkei 225 index in the last year so far the highlight of the performance。
While doubts have been expressed about the persistence of a series of easing measures, including the YCC policy, the Bank of Japan has remained motionless on the issue。According to a summary of the June meeting of the Bank of Japan's Review Committee released on Monday, the bank will continue its accommodative monetary policy, keeping policy rates unchanged, while not making adjustments to YCC policy.。
Kazuo Ueda believes that the current economic uncertainty is still very high, sustained and stable realization of the 2% price increase target "will take time."。Unlike the three countries mentioned above, Ueda here refers to "maintaining the price increase target at 2%," indicating that the Bank of Japan aims to maintain the country's inflation rate above 2% and stimulate inflation.。According to preliminary statistics from Japan's Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare in April, real wages fell 3.0%, 13 consecutive months of year-on-year decrease。
From this perspective, Japan has become the last samurai among the major developed economies to maintain loose monetary policy.。
·Original
Disclaimer: The views in this article are from the original Creator and do not represent the views or position of Hawk Insight. The content of the article is for reference, communication and learning only, and does not constitute investment advice. If it involves copyright issues, please contact us for deletion.