Economists: market misinterpretation of U.S. July PCE data rate hike cycle may be over
Therefore, for the year-on-year data, the inflation data for the same period last year will have a significant impact on the trend of the PCE data released this time, which is also known as the "base effect."。
Last week, the U.S. personal consumption expenditure index (PCE) data for July was released.。U.S. core PCE edged higher in July, up 0% month-on-month, driven by services such as financial services and insurance programs.2%, up 4.2%。However, according to the latest explanation from economists, the market's judgment of higher inflation is actually a misreading。
Year-over-year PCE data may be misleading under base effect
The misleading nature of the data stems from the statistical methods of PCE data.。PCE data publishes both year-on-year and month-on-month data calibers, with year-on-year meaning to compare July 2023 data with July 2022 data; and month-on-month meaning to compare July 2023 data with June 2023 data。
Therefore, for the year-on-year data, the inflation data for the same period last year will have a significant impact on the trend of the PCE data released this time, which is also known as the "base effect."。Economists say that as U.S. gasoline prices ushered in a wave of plunges in the same period last year, this factor indirectly raised the level of year-on-year inflation in the U.S. in July this year。
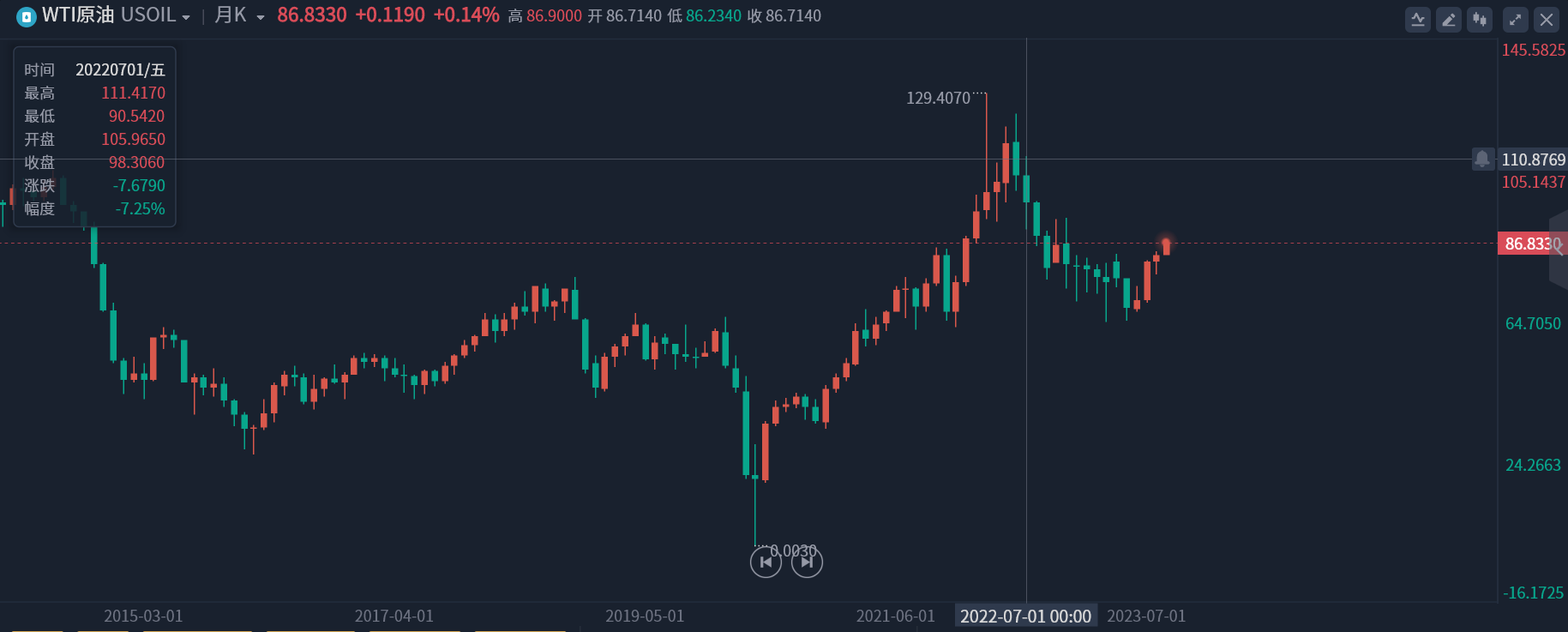
Jared Bernstein, chairman of the White House Council of Economic Advisers, believes that the year-on-year increase in inflation data does not mean that the month-on-month increase is widening, and the market needs to include the level of inflation in the same period last year.。Looking back at WTI crude oil trends, U.S. oil was sluggish last summer, and last July, the commodity fell 7% in a single month..25%, oil prices fell below $100 to close at 98.3060 USD / barrel。
From the more reliable ring data, the U.S. core PCE in July actually only slightly higher 0.2%, unchanged from June's growth rate。Taken together, this is already the smallest consecutive increase in PCE data since 2020, representing the Fed's effective inflation governance。
And the level of inflation in the United States is likely to weaken further.。
U.S. Student Loans Will Restart Payments From Next Month
At present, the current high interest rate policy in the United States has effectively depressed consumer demand for goods and services, not to mention entering October, the United States will restart the payment of student loans。
Due to the high cost of tuition at American universities, many families have to apply for student loans to help their children finish college。In 2020, about 68 percent of undergraduate students applied for federal student aid, according to the Office of Federal Student Aid, which includes federal loans, grants and work-study programs.。
Under U.S. government regulations, the U.S. government can suspend student loan repayment in the event of financial difficulties, emergencies, or other special circumstances。During the new crown epidemic, the Biden administration announced a moratorium on student loan repayments.。This fall, the repayment action is about to restart, specifically, the interest on federal student loans will begin to accumulate on September 1, and the first repayment after the suspension will start in October。

According to Experian, a total of 45 million people in the U.S. are now saddled with student loan debt, totaling about 1.7 trillion dollars。Many market participants have expressed concern about the potential impact on the economy of resuming student loan payments, especially on consumer spending and household finances.。Because the return of student loans may increase the default of family debt.。
In addition, U.S. inflation-adjusted consumer spending rose by just 0 percent in July after recording strong gains in June..6%。This means that Americans have been forced to use their savings to keep spending.。Data show that the U.S. savings rate has fallen to 3 last month.5%, the lowest level since November。
Economists: Fed tightening cycle is over
Faced with this situation, Gregory Daco, chief economist at EY-Parthenon, said consumer demand for goods and services will weaken as high interest rates and student loan repayments resume after being suspended during the epidemic, which will help reduce the level of full-year inflation in the United States.。
Weak consumer spending, combined with "weak" housing inflation and slower wage growth, should cause the Fed's favorite measure of inflation to fall for all of 2023, Daco suggested.。The economist expects overall PCE inflation to reach around 3% by the end of the year, with core PCE inflation at 3.6% to 3.Between 7% - a number that should stop the Fed from raising interest rates。
Kayla Bruun, senior economist at Morning Consult, agrees that the momentum in consumer spending "may fade in the fall," especially for spending on non-essential items and services from airline tickets to big-ticket items such as televisions.。
Bruun said that according to data from Morning Consult, the recent spending strength has been concentrated in discretionary categories, which are the most vulnerable to budget cuts when financial pressures increase.。Factors such as rising credit card interest rates, slowing wage growth, and the resumption of student loan repayments are likely to increasingly discourage the purchase of these non-essential items, thereby reducing the rate of income growth。
Bruun concluded: "The latest evidence of slowing consumer spending, easing labor market tensions, cooling wage growth momentum and slowing core inflation reinforces our expectations that the Fed's tightening cycle is over.。"

·Original
Disclaimer: The views in this article are from the original Creator and do not represent the views or position of Hawk Insight. The content of the article is for reference, communication and learning only, and does not constitute investment advice. If it involves copyright issues, please contact us for deletion.