Forex VS Stocks VS Indices Trading: Which Is Right for You?
Almost everyone that starts to trade usually jumps into trading forex markets.But should you really trade forex instead of stocks or indices?

In the financial markets, Forex (foreign exchange), stocks, and indices are the most common asset classes for trading. Each market has its own unique characteristics and trading conditions. Understanding the differences in volatility, leverage and margin requirements, liquidity, trading hours, and commissions can help traders choose the market that best suits their needs.
This article provides an in-depth comparison of Forex, stocks, and indices based on these aspects to aid in making informed trading decisions.
1. Volatility
Forex Market
The volatility in the Forex market is generally lower, especially for major currency pairs. For instance, the average daily volatility for EUR/USD over the past 12 months is 0.24.
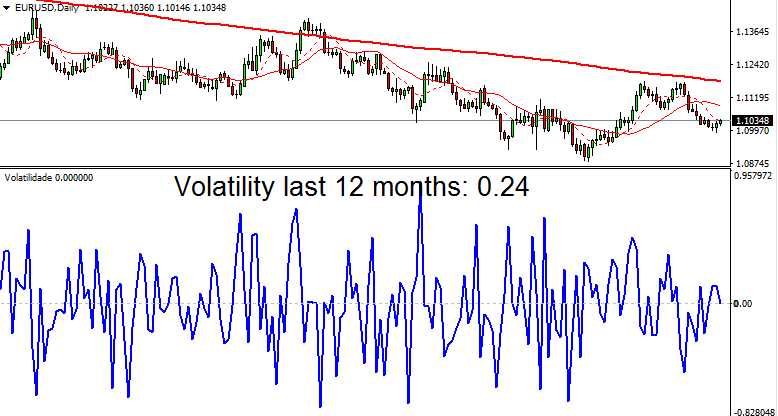
GBP/USD and GBP/JPY have volatilities of 0.38 and 0.41 respectively. Although these currency pairs are relatively active, their volatility is lower compared to stocks and indices.
Stock Market
The stock market typically exhibits higher volatility. For example, Apple Inc. (stock symbol: AAPL) has a volatility of 1.21, while Meta Platforms Inc. (formerly Facebook, stock symbol: META) has a volatility of 1.29.
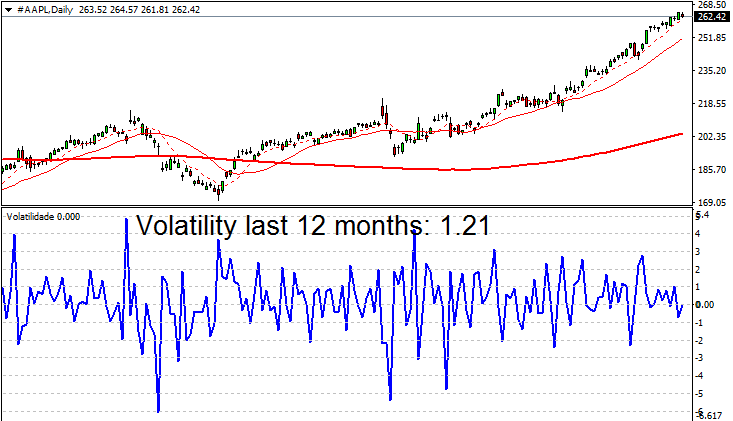
This data shows that stock market volatility is more than twice that of Forex and indices, making stocks particularly attractive for day traders and high-frequency traders.
Indices Market
The volatility of indices falls between Forex and stocks. For instance, the German DAX index has a volatility of 0.70, which is higher than Forex but lower than individual stocks.
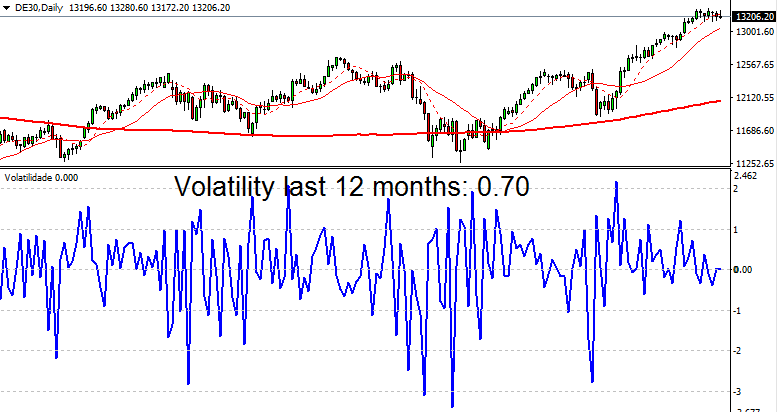
The Dow Jones Industrial Average (DJIA) has a volatility of 0.60.
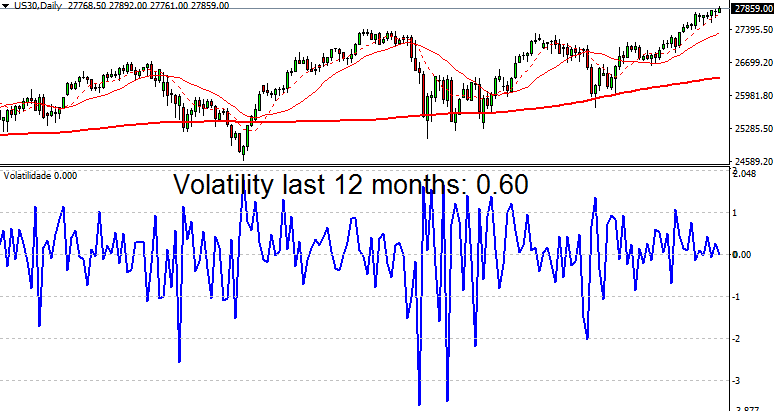
Overall, stock markets exhibit the highest volatility, followed by indices, with the Forex market having the lowest volatility. When choosing a trading market, it is important to consider how volatility affects your trading strategy and profit potential.
2. Leverage and Margin
Leverage and margin have an inverse relationship, i.e. when leverage increases the required margin decreases and vice versa.
Forex Market
The Forex market offers the highest leverage, often up to 1:1000. This means that traders can control a $1000 Forex trade with just $1 of their own funds. While high leverage can amplify profits, it also magnifies risks. Margin requirements are relatively low, but effective risk management is crucial.
Indices Market
The leverage available in indices trading is typically up to 1:200. This allows traders to control larger positions with less capital, offering greater flexibility compared to stocks, but still carries leverage risk.
Stock Market
Leverage in stock trading is usually the lowest, around 1:20. This requires traders to invest more capital to enter trades, making it less suitable for day trading compared to Forex and indices.
When choosing leverage and margin requirements, traders should adjust their leverage based on their risk tolerance and capital availability. Excessive leverage can lead to significant losses, so prudent leverage use is essential.
Usually used for the margin and leverage required to trade forex, indices and stocks:
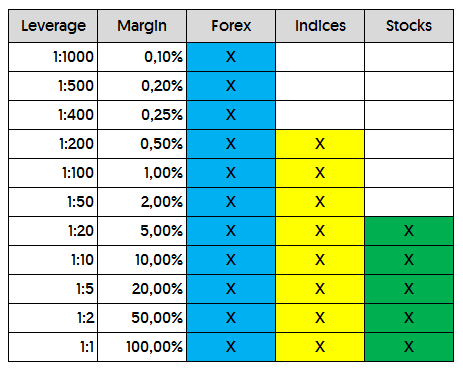
Regulations on leverage vary from region to region. The European Union has a leverage limit of 1:30 for major currency pairs due to ESMA, and the United States has a leverage limit of 1:50 for major currency pairs.
3. Liquidity
Forex Market
The Forex market is the most liquid market globally. For example, EUR/USD sees a massive daily trading volume and extremely high liquidity. This results in narrow bid-ask spreads and minimal slippage.
Stock Market
Liquidity in the stock market varies depending on the specific stock. Major blue-chip stocks such as Apple Inc. (AAPL) and Microsoft Corporation (stock symbol: MSFT) usually have very high liquidity, while smaller or penny stocks may have lower liquidity. Insufficient liquidity can lead to larger bid-ask spreads and slippage.
Indices Market
Major indices like the DAX and DJIA also have high liquidity. Highly liquid indices tend to have smaller bid-ask spreads and lower trading costs.
In general, the Forex market offers the highest liquidity, followed by major stocks and indices. Choosing a market with high liquidity can reduce trading costs and minimize slippage due to liquidity issues.
4. Trading Hours
Forex Market
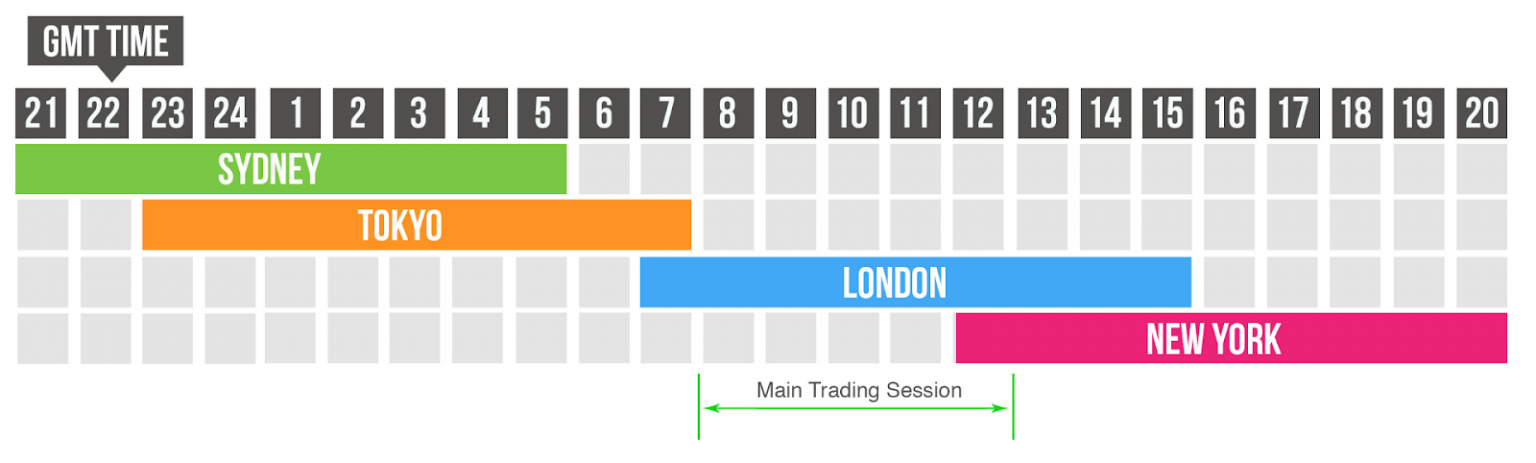
The Forex market operates 24 hours a day, covering three major trading sessions: Asian, European, and American. The best trading times are often during the overlap of major markets, such as the London and New York sessions, which provide higher market volatility and liquidity.
Stock Market
Stock trading hours depend on the specific stock exchange. For example, the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) and NASDAQ open from 9:30 AM to 4:00 PM Eastern Time, while the London Stock Exchange (LSE) operates from 8:00 AM to 4:30 PM GMT.
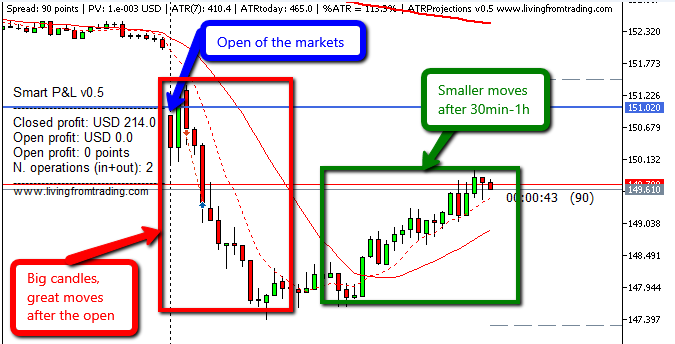
While some brokers offer after-hours trading, activity during these periods is typically lower. Stock can only be traded during exchange opening hours, and the hour after the opening of the market is usually the best time to trade shares.
Indices Market
The best trading times for indices align with the corresponding exchange hours. For instance, the optimal trading time for the DAX is the first 1-2 hours of the London trading session, while the DJIA and S&P 500 are best traded during the first 1-2 hours of the New York market.
Traders should plan their trading around market open times to take advantage of the most active trading periods and maximize trading opportunities.
5. Commissions
Commission can significantly affect trading performance, potentially determining whether you make a profit.
Commission vs. Spread
- Commission: Fees charged at the opening and closing of trades.
- Spread: The difference between the buying and selling prices. Brokers with no commission typically have higher spreads, while those charging commissions often have lower spreads.
Examples
-
Stock Trading: Broker A charges a $20 commission per 100 shares with a spread of $0.05. Broker B has no commission but a spread of $0.30. After calculating the “effective spread,” choosing the broker with lower commission is generally more advantageous.
-
Forex Trading: Broker A charges a $7 commission per lot with a spread of 0.2 pips. Broker B has no commission but a spread of 1.0 pips. After calculating the “effective spread,” brokers with lower commissions tend to be more favorable.
Conclusion
Forex, stocks, and indices each have their unique trading characteristics. The best market for you depends on your trading style, risk tolerance, and capital availability:
- Forex Market: Suitable for traders with smaller capital, offering high leverage and high risk but very high liquidity.
- Stock Market: Suitable for traders with larger capital, offering high volatility and trading opportunities but lower leverage.
- Indices Market: Offers moderate leverage and capital requirements with moderate volatility, suitable for most traders.
Choosing the right market depends on individual trading goals and risk preferences, allowing you to achieve optimal investment outcomes.
Disclaimer: The views in this article are from the original Creator and do not represent the views or position of Hawk Insight. The content of the article is for reference, communication and learning only, and does not constitute investment advice. If it involves copyright issues, please contact us for deletion.