Europe, the United States and the United Kingdom this round of monetary policy review & outlook: continue to raise interest rates or pause the pace?
In the wake of this protracted and inflationary battle around the world, the policy environment facing central banks has changed a lot from before the rate hike cycle began.。
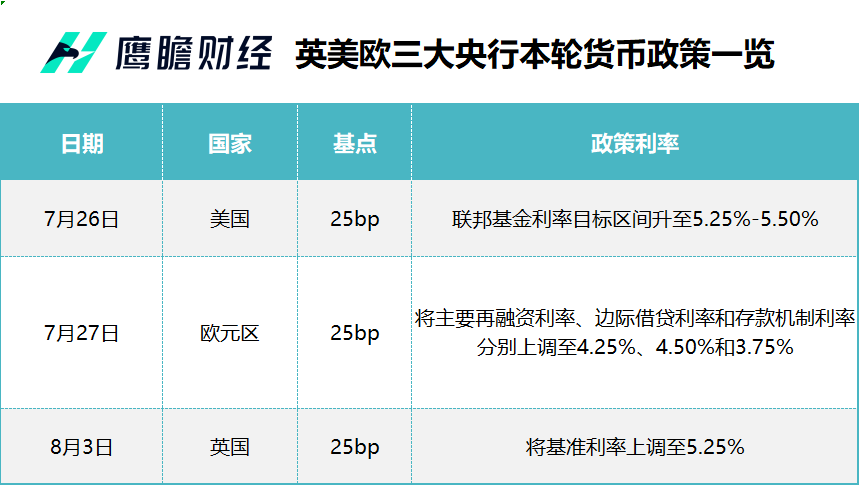
In July, central banks in Europe and the United States carried out interest rate hikes as scheduled。On August 3, the Bank of England also raised its policy rate by 25BP to 5.25%, and heralds the possibility of further rate hikes。In the wake of this protracted and inflationary battle around the world, the policy environment facing central banks has changed a lot from before the rate hike cycle began.。
U.S.: U.S. debt demand side challenged non-farm payrolls data less than expected
Entering August, the U.S. Treasury Department took the lead in stepping on mines。On August 1, Fitch (Fitch) announced that it would downgrade the default rating of long-term foreign currency issuers in the United States from 'AAA' to 'AA +' and demonstrated concerns about the deterioration of the U.S. financial situation over the next three years.。

Fitch believes that governance standards in the United States have steadily deteriorated over the past two decades, including on fiscal and debt issues.。Repeated debt ceiling political gridlock and last-minute resolution sap confidence in U.S. fiscal management。In addition, unlike most similar countries, the United States Government lacks a medium-term fiscal framework and the budgeting process is complex。These factors, combined with several economic shocks, tax cuts and new spending plans, have led to successive increases in debt over the past 10 years.。
Fitch's move was met by U.S. Treasury Secretary Yellen (Janet L..Yellen) 's backlash。Yellen said Fitch's judgment ignores the resilience of the current U.S. economy, such as low unemployment, falling inflation, strong innovation, and improved governance during the Biden administration。Yellen also said Biden's June debt limit deal with Republicans included more than $1 trillion in deficit cuts over 10 years, and that Fitch's downgrade was based on outdated information.。
Still, according to the U.S. Treasury's third-quarter financing plan on July 31, the Treasury will borrow about $1 trillion in debt in the third quarter of this year, about $274 billion more than previously announced plans to issue debt, a level that is already significantly higher than the size of the financing announced in May.。In addition, according to the plan, in the fourth quarter, the department is expected to borrow about $852 billion more in debt, which is another nearly $100 billion debt surge.。
Market participants are spending, and part of the reason the U.S. Treasury is stepping up its debt issuance is that the Treasury is now paying higher interest rates on its debt and its tax revenues are lower than expected。The Fed, meanwhile, is reducing its holdings of Treasuries by up to $60 billion a month, forcing the government to sell more bonds to other buyers.。
In other words, in the face of this huge financing plan, even though Yellen was one of the key figures in the previous push to suspend the debt ceiling bill, her criticism of the Fitch downgrade also appeared slightly untenable.
A staggering figure is that as early as June of this year, the size of the U.S. federal government's debt exceeded $32 trillion.。After breaking the debt ceiling again, the market expects that by 2030, the size of the U.S. national debt will exceed $50 trillion, which is a pretty scary number - in 2022, the U.S. will have a full-year GDP of 25.$46 trillion, and that figure is almost twice that.。
The U.S. Treasury's sharp increase in debt challenges the pressure on the demand side of U.S. debt to digest the supply of long bonds, and U.S. exhibition yields have continued to rise recently.。On August 2, ADP employment exceeded expectations, and 10-year U.S. bond yields directly broke 4.1%。Two days later, another employment report, the U.S. non-farm payrolls data for July, new jobs for the second month in a row below 200,000, but hourly wages rose month-on-month, U.S. bond 10-year yields rose 4.Falling back after 2%。
Watch this nonfarm payrolls report, U.S. nonfarm payrolls added in July 18.70,000, lower than expected; unemployment falls back to 3.5 per cent; labour force participation rate 62.6%, unchanged from the previous value; July hourly earnings, which the Fed is particularly concerned about, rose 4% year-on-year..4%, up 0.4%, both unchanged from the previous period, representing wage stickiness still in place and inflation still at risk of rising。
For now, Fed officials are somewhat ambiguous about the future of monetary policy。Earlier, Minneapolis Fed President Neel Kashkari said the outlook for inflation in the United States was "fairly optimistic," although aggressive monetary tightening by the central bank to curb price spikes could lead to some job losses and slower growth.。He believes that future rate hikes will be based on the data and the Fed will continue to raise rates if needed.。
Another FOMC voting committee, Chicago Fed President Austan Goolsbee, said there would be no pre-commitment to the September FOMC vote because it was too early to say what should be done at the next policy meeting.。He believes that inflation will fall at a reasonable rate, while the unemployment rate will not rise sharply.。While recent data has given it hope that inflation can cool without causing too much pain to the economy, it wants to see more trend developments before stopping rate hikes.。I've seen progress in short periods of time before, like last summer, but it turned out to be a false improvement。
Atlanta Fed President Raphael Bostic (Raphael Bostic) has begun to dove, that the Fed does not need to continue to raise interest rates in September。He urged the Fed not to tighten monetary policy too much as inflation may continue to recede。In his eyes, inflation is well below the highs seen last year, with recent data promising that inflation may be seen to continue to fall。
However, he also noted that while the benchmark view has not changed, the Fed will get a lot of additional data by September and is willing to adjust his view of that meeting if the data is contrary to his expectations.。
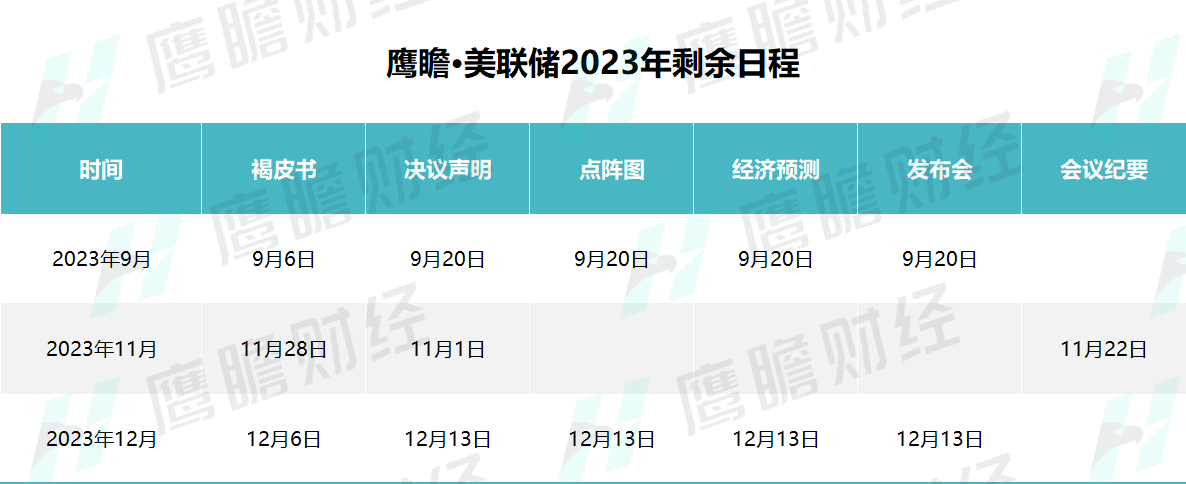
The Fed will hold three more monetary policy meetings for the rest of the year。Among other things, at its September and December meetings, the Fed gives its quarterly economic forecast and dot plot。
Eurozone: Economic activity has slowed Lagarde is open to September policy
In the euro area, on July 27, according to the European Central Bank's monetary policy meeting, the bank decided to raise all three key interest rates in the euro area by 25 basis points: the main refinancing rate, the marginal lending rate and the deposit mechanism rate to 4.25%, 4.50% and 3.75%。
Although the central banks of Europe and the United States are raising interest rates, but the difference between the two is that under the governance of the Federal Reserve, the level of inflation in the United States has been cut in half from its peak, the market debate about the Fed's upcoming end of the interest rate hike window is buzzing, but, on the ECB's side, the core inflation rate in the euro area is still strong, the purchasing power of the euro is still declining rapidly, and。
Eurozone inflation eased in July, with consumer prices up 5.3%, compared with a 5% increase in June.5%。Worryingly, core inflation in the euro area, which excludes seasonal factors and fluctuations in raw material prices, remains at 5.5%, higher than economists expected。
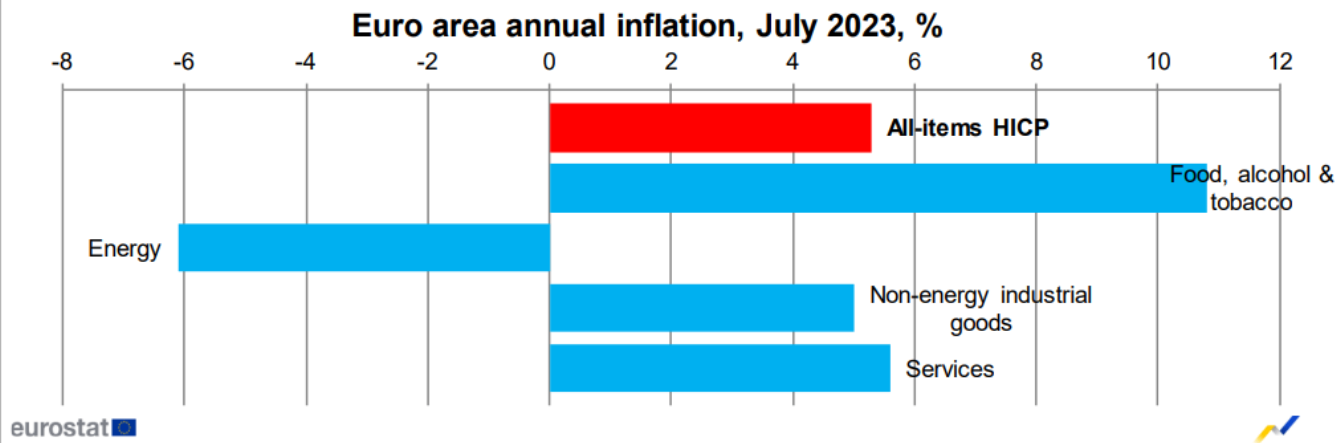
The ECB believes that inflation will remain too high for a long time, and the driving force of inflation is changing。Specifically, internal price pressures, including rising wages and strong profit margins, are replacing external pressures as an important driver of inflation growth in the region.。
To curb high inflation, the ECB has raised interest rates nine times in a row since July last year, for a total of 425 basis points.。Analysts believe that the European Central Bank has recently released two important signals on the direction of monetary policy in the euro area: first, the final level of interest rates for this round of interest rate hikes is likely to be higher than previously expected;。
High interest rates combined with high inflation have a dampening effect on economic activity.。Eurozone business confidence index has been falling since February。The Eurozone Manufacturing Purchasing Managers Index (PMI) also continued to decline, reaching 42 in July..7, a three-year low。In addition, according to the ECB's credit survey, demand for commercial loans in the region also fell to an all-time low on record in the second quarter.。
From the fiscal policy point of view, the current level of public debt in European countries is generally at an all-time high, member states through the expansion of government spending to stimulate the economy has been very limited, which may force the ECB officials to consider more accommodative monetary policy, such as: pause the interest rate hike cycle.。
In fact, ECB President Christine Lagarde (Christine Lagarde) did not give forward guidance to the September meeting at a press conference after the July interest rate decision, saying that there is a possibility of "opening up" monetary policy in September.。
UK: Eagles rumble after interest rate decision expected to continue to raise interest rates in September
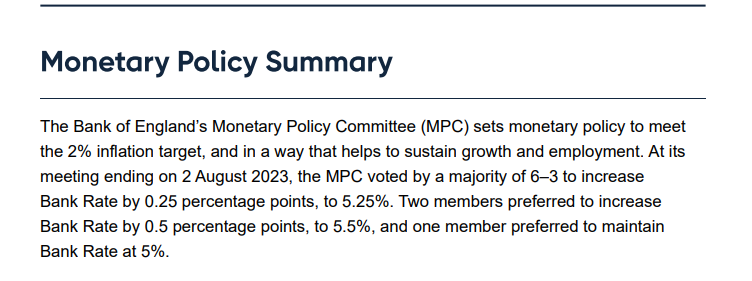
The Bank of England, for its part, also acknowledged its stance on restrictive interest rates after the rate hike and said it would continue to closely monitor signs of continued inflationary pressures and overall economic resilience: "If there is evidence that pressures persist, then further monetary policy tightening is needed."。
Currently, the UK's CPI is still well above the 2% target, with stronger-than-expected CPI inflation for both services and core goods。According to the BoE, inflation is expected to fall to 5 per cent by around the end of the year as energy price inflation falls, followed by food and core commodity price inflation.。By early 2025, inflation is expected to stay at 2.25%。
After the rate decision was announced, the Bank of England mostly hawked officials and is expected to continue its rate hike action in September。
Among other things, the Bank of England's deputy governor, Ben Broadbent, said we must ensure that inflation falls sustainably to the target level, so given the information we currently have, we must focus on ensuring that average interest rates are sufficient to ensure that this is achieved.。· · · · · Our focus is on the medium term and we must (ensure) that interest rates during this period are sufficiently restrictive。
Andrew Bailey, the governor of the Bank of England, agrees that it is too early to say that interest rates have peaked.。He believes that inflation is expected to fall further in the July data, and core commodity inflation will ease for the rest of the year.。In his eyes, the upward surprise in wage inflation suggests that it will take longer for the second round of effects to disappear than the sharp rise in imported commodity prices in 21-22.。The rest of the labor market is weakening, but the pay factor is not.。
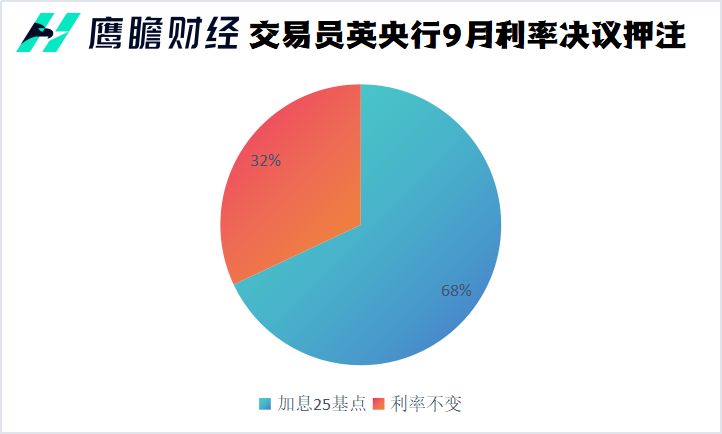
It is reported that after the decision of the Bank of England, traders expect the probability of raising interest rates by 25 basis points at the September meeting is 68%, and the probability of keeping interest rates unchanged is 32%。
·Original
Disclaimer: The views in this article are from the original Creator and do not represent the views or position of Hawk Insight. The content of the article is for reference, communication and learning only, and does not constitute investment advice. If it involves copyright issues, please contact us for deletion.