Average Japanese wages rise 5.28% of the market ushered in the dawn of interest rate hike?
The pay rise, the highest in 33 years and far more than expected, may prompt the Bank of Japan to take rate hikes, ending eight years of negative interest rate policy。
On March 15, Japan's largest trade union organization, the General Federation of Trade Unions of Japan (Rengo), announced that Toyota, Japan's largest company, will raise labor pay by 5 percent in 2024 through union negotiations and bids..28%, or 16,469 yen (about $110) per month, far more than 3 a year ago..8%, the largest increase since 1991。
It was earlier reported that the pay rise, which is the highest in 33 years and far more than expected, may prompt the Bank of Japan to take measures to raise interest rates, ending eight years of negative interest rate policy.。
Every spring, Japanese unions and management hold annual pay negotiations, known as "spring fights" or "spring offensives," to set monthly wages for laborers before the start of Japan's fiscal year in April.。This negotiation is one of the characteristics of Japanese companies and is fundamental to the fact that Japanese companies' labor relations are more collaborative than those of other countries.。
For decades, Japan's wage growth has been sluggish, and the government has attributed part of its economic woes to it。Since taking office, Prime Minister Fumio Kishida has urged businesses to raise basic wages faster than inflation, boosting household spending, helping lift Japan out of years of deflation and bring more lasting growth to the economy, ending a situation where wage growth has lagged far behind the average of rich OECD countries.。
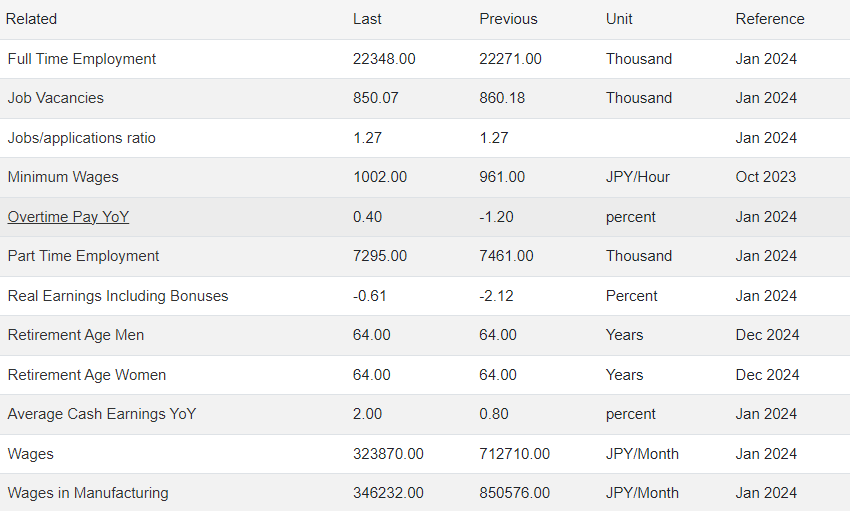
At the end of last year, Japan's economy barely emerged from recession.。But while Japanese companies have been raising wages, the increases have largely failed to keep pace with inflation.。Statistics show that inflation-adjusted real wages have now fallen for 22 consecutive months。
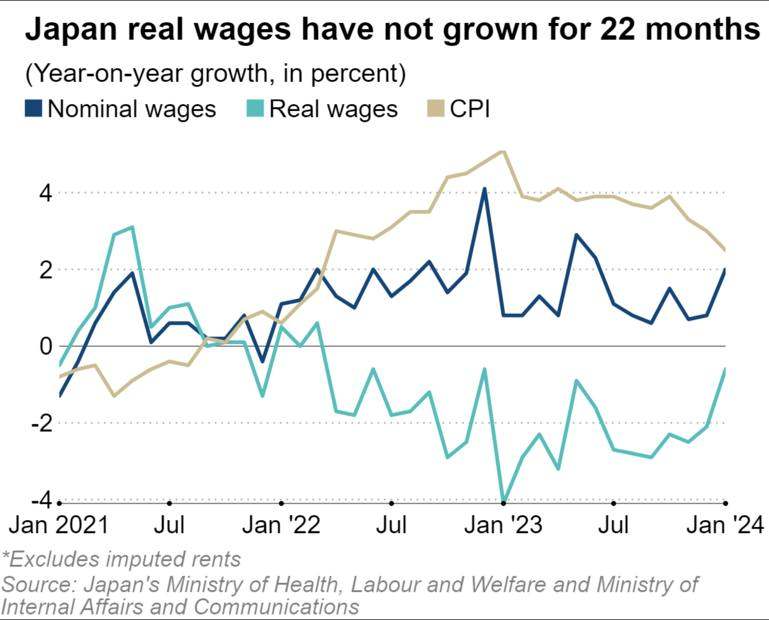
In recent years, central banks around the world have taken rate hikes in the face of soaring inflation, but the Bank of Japan has maintained negative interest rates and other policies to boost the economy, leading to a sharp depreciation of the yen against the dollar.。The wave of wage increases comes against a backdrop of rising labor shortages, persistent inflation and increased profits for export-oriented companies due to the weak yen.。
Even so, the Bank of Japan stressed the need to see wage increases and sustained 2 per cent inflation data to achieve a "virtuous cycle" before shifting the wind.。Bank of Japan Governor Kazuo Ueda called the spring talks an "important moment" to consider when and how to achieve this much-anticipated shift.。
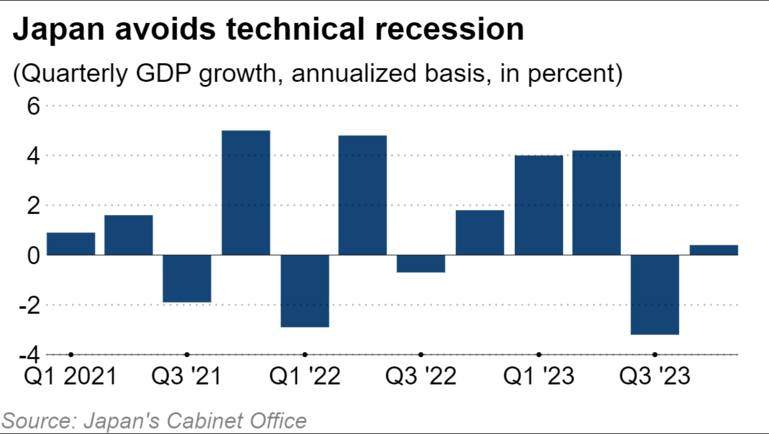
Today, an environment conducive to central banks considering monetary reform has quickly emerged。March 11, Japan's latest gross domestic product data showed that Japan has narrowly emerged from a technical recession, the data further strengthened market confidence。
According to relevant sources, the Bank of Japan has begun internal and external coordination on interest rate hikes to end the ultra-loose monetary policy adopted since February 2016.。
However, the Bank of Japan has repeatedly stated that it will maintain loose monetary policy in the future even if it takes interest rate measures.。After 17 years, the bank's return to the path of raising interest rates does not mean that it has control over the money supply, but only a corresponding reduction in stimulus measures, and the cautious move has created a good environment for companies to raise wages.。

·Original
Disclaimer: The views in this article are from the original Creator and do not represent the views or position of Hawk Insight. The content of the article is for reference, communication and learning only, and does not constitute investment advice. If it involves copyright issues, please contact us for deletion.