What is Dividend Yield?
Dividend yield is a tool for comparing the size of a company's dividend to its share price.It's the annual dividend divided by the stock price.However, a higher dividend doesn't always signal a high potential investment.

Dividend yield is an important financial metric that compares a company's annual dividend payments to its current stock price, expressed as a percentage. The formula is:
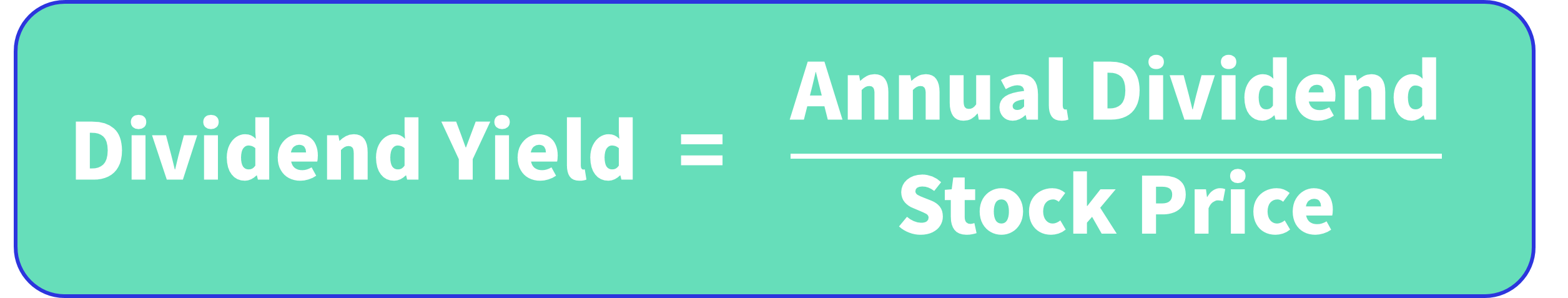
The Role of Dividend Yield
Dividend yield helps investors assess a stock's attractiveness. A higher dividend yield typically indicates that a stock provides a greater cash return relative to its price, which is particularly appealing for income-seeking investors. However, a high yield does not always imply a financially healthy company; it may appear inflated due to a drop in stock price.
How to Calculate Dividend Yield
Calculating dividend yield involves several steps, depending on the frequency of the company’s dividend payments. For example, consider The Walt Disney Company (NYSE: DIS) as of July 12, 2019:
- Stock Price: $144.88
- Semiannual Dividend: $0.88 (paid on January 10, 2019, and July 25, 2019)
- Annual Dividend Calculation: $0.88 × 2 = $1.76
- Dividend Yield Calculation:
This example clearly illustrates how to compute dividend yield based on the relationship between dividends and stock price.
The Relationship Between Dividend Yield and Total Return
Dividend yield is a crucial component in evaluating investment returns but should not be used in isolation. Total return encompasses both the dividend yield and the change in stock price, calculated as:
For instance, if a stock has a dividend yield of 2% and its price increases by 5% over the year, the total return would be 7%. Conversely, if the stock price declines, the total return may turn negative, even if dividends are still paid.
Difference Between Dividend Yield and Payout Ratio
-
Payout Ratio: This indicates the percentage of net income used for dividends. The formula is:

It shows how much of the company's profits are allocated to dividend payments.
-
Dividend Yield: Focuses on the relationship between the value of the dividends and the current stock price, providing insight into the cash returns received by shareholders from their stock investments.
Limitations of Dividend Yield
While dividend yield is a useful tool for assessing investment value, it has limitations:
- Price Volatility Impact: A high dividend yield might result from a decline in stock price, which does not necessarily indicate strong company fundamentals.
- Short-term Fluctuations: Changes in dividend yield can be influenced by short-term market volatility, leading to misinterpretations.
- Dividend Policy Changes: Companies may adjust dividend payments based on their operating performance, affecting investor return expectations.
Therefore, investors should consider multiple indicators when assessing potential investments, including company profitability, historical dividend payments, and debt levels, for a comprehensive analysis.
Characteristics of Companies with High Dividend Yields
High dividend yields are often found in the following types of companies:
-
Mature and Stable Enterprises: These companies are typically in the later stages of their lifecycle, with stable cash flows that enable them to maintain dividend payments. Examples include consumer goods giants like Coca-Cola (NYSE: KO) and Procter & Gamble (NYSE: PG), which continue to perform well amid economic fluctuations.
-
Specific Industries: Utility companies and Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) often exhibit high dividend yields due to their stable demand and business models, even in challenging economic conditions.
-
Regulated Income Companies: Some companies, such as REITs, are structured to distribute a large portion of their income as dividends, which leads to high dividend yields. These firms not only provide attractive returns but also stable cash flows.
·Original
Disclaimer: The views in this article are from the original Creator and do not represent the views or position of Hawk Insight. The content of the article is for reference, communication and learning only, and does not constitute investment advice. If it involves copyright issues, please contact us for deletion.