What is Net Profit Margin?
The net profit margin is one of the essential calculations used to determine a company’s financial health — it refers to the percentage of profit a company earns out of its total overall revenue.

Net profit margin is a key financial metric used to assess a company's financial health, typically represented as the ratio of net profit to total revenue. Net profit refers to the earnings remaining after all expenses, costs, taxes, and other expenditures are deducted, while total revenue encompasses all sales income generated by the company over a specific period. The formula for calculating net profit margin is as follows:
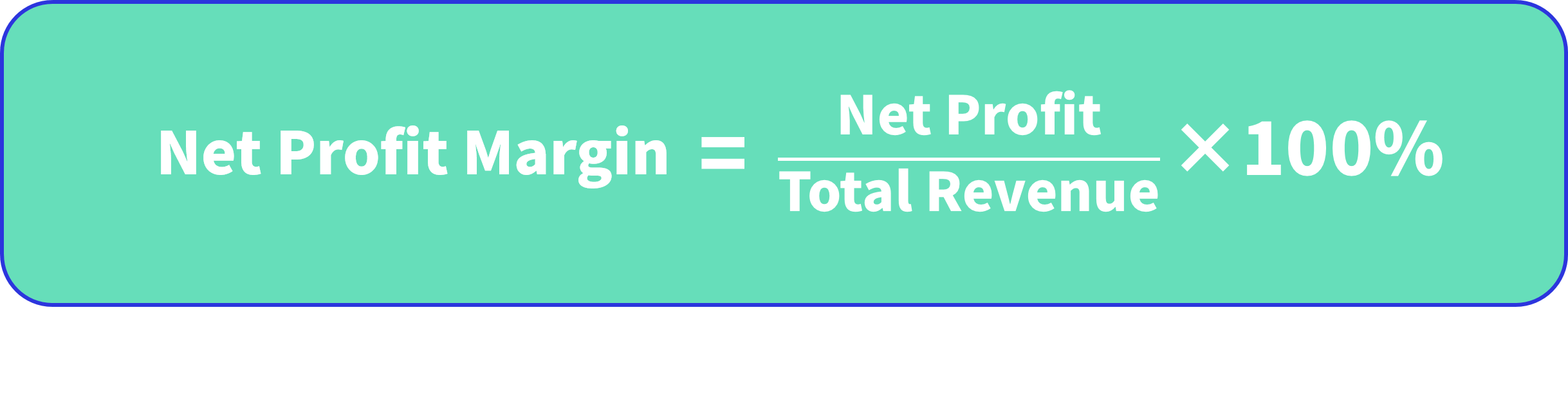
This metric allows investors and management to quickly understand the company's profitability and cost control efficiency.
How to Calculate Net Profit Margin
-
Data Acquisition: To calculate the net profit margin, relevant data must be extracted from the company's financial statements. Publicly traded companies typically detail this information in their annual and quarterly reports.
-
Calculating Net Profit: Net profit is usually the figure obtained by subtracting all relevant costs and expenses from total revenue. It should include operating profit, interest income, interest expenses, and taxes.
-
Calculating Total Revenue: Total revenue consists of all income earned from the sale of goods or services during a specific period.
-
Applying the Formula: Substitute net profit into the formula to compute the net profit margin.
For example, if a company has total revenue of $5 million and total operating costs and other expenses amount to $4 million, its net profit would be $1 million. According to the formula, the net profit margin would be:
This result indicates that for every dollar of revenue earned, the company retains 20 cents as profit.
Difference Between Net Profit Margin and Gross Profit Margin
Net profit margin differs from gross profit margin in that the latter focuses solely on profits remaining after the cost of goods sold, while the former takes into account all expenses, including operational costs, taxes, and other expenditures. Specifically:
- Gross Profit Margin focuses on the revenue remaining after the sale of goods.
- Net Profit Margin considers the final profitability after all expenses.
For instance, in a retail business, the cost of goods sold (COGS) includes the costs associated with the sold items, while net profit includes all operational expenses like rent, salaries, and technology costs.
Industry Standards for Net Profit Margin
There are no fixed standards for what constitutes a "good" net profit margin, as it varies with industry characteristics and market conditions. For example, the net profit margin in the consumer goods sector may be relatively low, whereas in technology or pharmaceutical sectors, it tends to be higher. Understanding industry averages and competitor performance is crucial when analyzing net profit margins.
Common net profit margin ranges by industry include:
- Retail: Typically between 3% and 5%.
- Manufacturing: Generally between 10% and 20%.
- Technology: Can be as high as 20% to 30%.
- Pharmaceuticals: May reach 15% to 30% or higher.
Importance of Net Profit Margin
-
Indicator of Financial Health: Net profit margin serves as a measure of a company's financial health, helping investors and management gauge profitability and cost control efficiency.
-
Support for Decision Making: Companies can formulate business strategies based on net profit margin, such as optimizing cost structures, adjusting pricing strategies, or reallocating resources.
-
Investment Decision Reference: Investors often consider net profit margin when evaluating potential investments, as a high net profit margin typically indicates a strong competitive advantage within the industry.
-
Performance Evaluation: Management can use net profit margin as a performance metric to identify successful business areas and those needing improvement.
Factors Affecting Net Profit Margin
-
Cost Control: Managing costs during production and operations is critical for enhancing net profit margin. By improving production efficiency, reducing raw material costs, and optimizing human resources, companies can significantly boost their margins.
-
Market Competition: Intense market competition can affect a company’s pricing power, thereby impacting net profit margin. If competitors lower prices, companies may have to follow suit to maintain market share, leading to decreased margins.
-
Economic Environment: Economic cycles influence consumer spending, which in turn affects sales revenue and net profit. During economic downturns, consumer spending typically declines, leading to reduced sales and profits.
-
Financial Leverage: The degree of debt financing directly impacts net profit margin. While appropriate debt can support expansion, excessive debt burdens increase interest expenses, thereby reducing net profit.
-
One-time Expenditures: Companies may incur one-time expenses during specific periods, such as asset disposal losses or restructuring costs, which can reduce net profit in that period and affect the margin.
Trend Analysis of Net Profit Margin
Analyzing the trend of a company’s net profit margin provides valuable insights for investors and management. By comparing net profit margins across different periods, stakeholders can assess the company’s growth and stability.
-
Long-term Trends: A consistent increase in net profit margin indicates effective cost management and revenue enhancement, often a favorable sign for investors.
-
Short-term Fluctuations: Short-term variations may be influenced by seasonal factors or one-time events. For example, a retail company might experience a temporary increase in net profit margin during the holiday season due to a surge in sales.
-
Industry Comparison: Comparing a company's net profit margin with peers in the same industry helps investors better understand its market position and competitive advantages.
In conclusion, net profit margin is a crucial financial indicator that reflects a company's profitability and aids management and investors in making informed decisions. By thoroughly analyzing the calculation methods, influencing factors, and industry standards of net profit margin, companies can better understand their financial health and maintain a competitive edge.
·Original
Disclaimer: The views in this article are from the original Creator and do not represent the views or position of Hawk Insight. The content of the article is for reference, communication and learning only, and does not constitute investment advice. If it involves copyright issues, please contact us for deletion.