What is a PE ratio?
A company's stock price is driven by its ability to generate profits.The P / E ratio compares those two things directly - It's the company's share price divided by its earnings per share.

The Price-to-Earnings Ratio (P/E Ratio) is an important financial metric used by investors to assess the value of a stock. It reflects how much investors are willing to pay for each dollar of earnings by comparing a company's stock price to its Earnings Per Share (EPS). The P/E ratio helps evaluate whether a stock is "expensive" or "cheap," making it an indispensable tool in stock market analysis.
Calculation of the P/E Ratio
The formula for calculating the P/E ratio is:
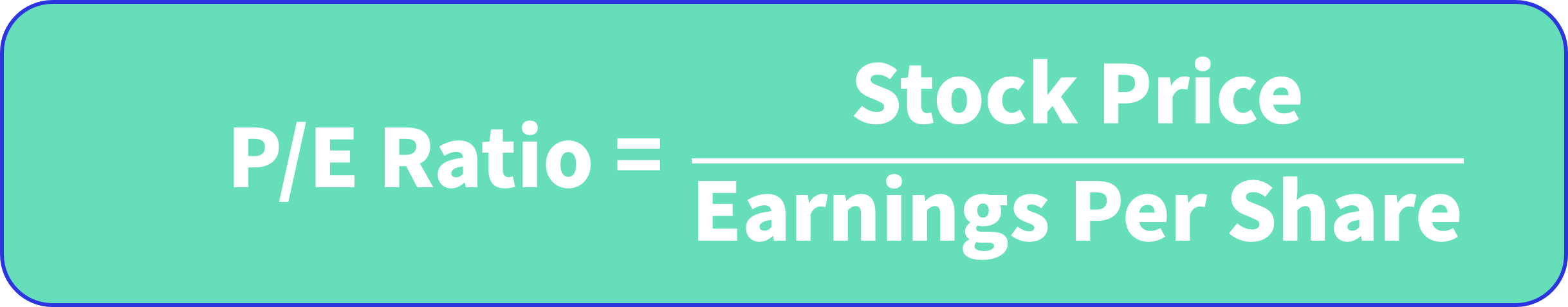
Example Analysis
For example, consider Apple Inc. (AAPL). Suppose at a certain point in time, Apple's stock price is $150, and its EPS for the past 12 months is $5. The P/E ratio would be calculated as follows:.
This indicates that investors are willing to pay $30 for every dollar of earnings, reflecting market expectations for future growth.
Significance of the P/E Ratio
The P/E ratio is not just a simple number; it represents market perceptions of a company's future earning potential:
-
High P/E Ratio: Typically indicates that the market is optimistic about the company's future growth. For instance, Tesla (TSLA) once had a P/E ratio exceeding 100, signaling that investors expected it to achieve robust growth.
-
Low P/E Ratio: May suggest a lack of confidence in the company's future profitability, especially if the company faces industry challenges or overall economic slowdowns. Some traditional energy companies might exhibit lower P/E ratios, reflecting investor skepticism about their future growth prospects.
Methods of Comparing P/E Ratios
Comparing P/E ratios can provide important decision-making insights for investors, primarily through the following methods:
-
Market Benchmark Comparison: Investors can compare an individual company's P/E ratio with that of the S&P 500 index. If a stock's P/E ratio is significantly higher than the S&P 500 average, it may indicate that the stock is overvalued.
-
Industry Average Comparison: Comparing a company's P/E ratio with the average in its industry helps investors determine whether the company's valuation is reasonable. For example, comparing Walmart (WMT)'s P/E ratio with the average for the retail industry can reveal its relative standing.
-
Peer Company Comparison: When analyzing multiple competing companies, comparing their P/E ratios can help investors identify which company may have more investment value. For instance, if Alphabet Inc. (GOOGL) has a lower P/E ratio than Amazon.com Inc. (AMZN), investors may further analyze the growth potential and risks associated with both companies.
Limitations of the P/E Ratio
Despite being a useful assessment tool, the P/E ratio has notable limitations:
-
Negative P/E Ratio: If a company is consistently unprofitable, its EPS will be negative, making the P/E ratio undefined. In such cases, the P/E ratio may not provide useful information, and a long-term negative P/E ratio may indicate poor financial health.
-
Lagging Historical Data: The P/E ratio is based on the past 12 months of EPS, which may not accurately reflect the company's current or future financial situation. Therefore, investors should analyze it alongside the latest market trends and company developments.
-
Industry Differences: P/E ratios can vary significantly across different industries, so it is essential to consider industry characteristics when comparing ratios. Technology companies typically have higher P/E ratios, while mature consumer goods companies may exhibit lower ratios.
-
Earnings Volatility: A company's earnings may be influenced by seasonal or cyclical factors, leading to fluctuations in EPS. As a result, a single period's P/E ratio may not represent the company's long-term financial performance.
·Original
Disclaimer: The views in this article are from the original Creator and do not represent the views or position of Hawk Insight. The content of the article is for reference, communication and learning only, and does not constitute investment advice. If it involves copyright issues, please contact us for deletion.