Will the resolution of the U.S. debt crisis be the last straw to crush the Fed's rate hike cycle??
On May 28, U.S. President Joseph Biden said he had reached an agreement on the debt ceiling with House Speaker Kevin McCarthy, and that the agreement would be submitted to the House of Representatives on May 31 for a vote.。
On May 28, after many twists and turns, U.S. President Joe Biden (Joseph Biden) said that an agreement has been reached on the debt ceiling issue and House Speaker Kevin McCarthy (Kevin McCarthy), and the agreement will be submitted to the House of Representatives on May 31.。
A seesaw end to the debt agreement is finally reached, with both parties having their own gains.
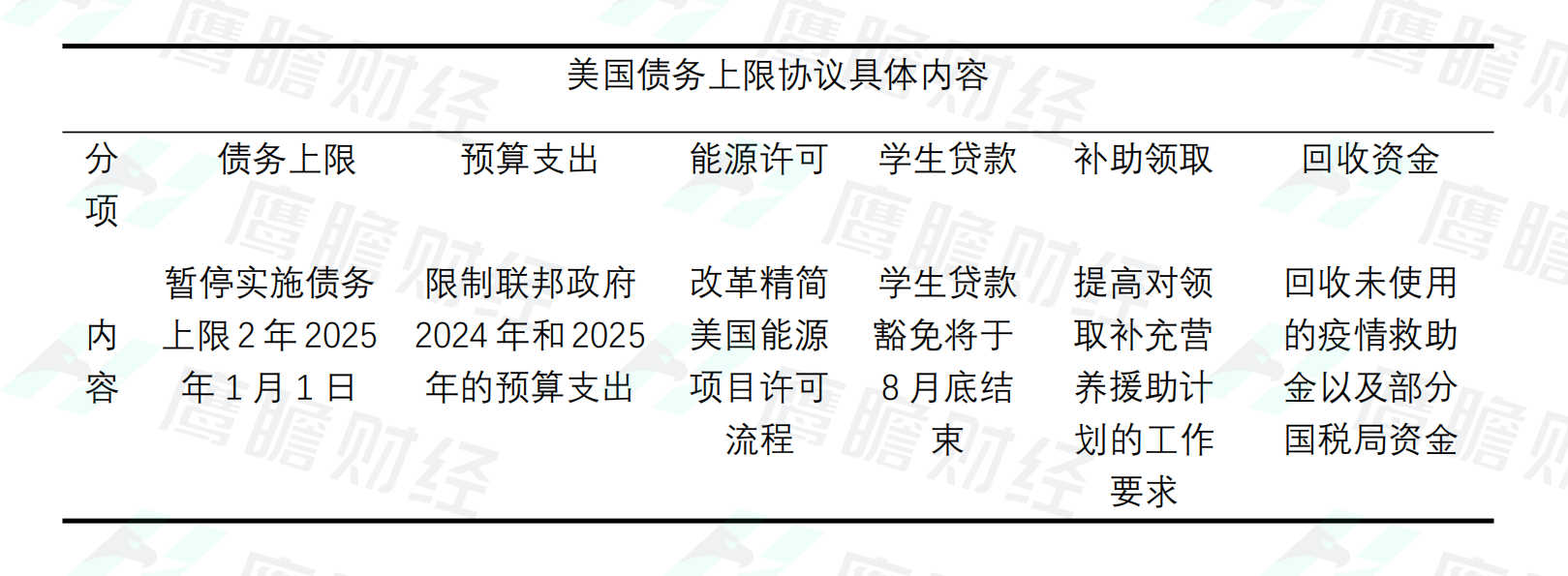
According to the agreement, the federal government's debt ceiling will be suspended for two years until January 1, 2025, but its non-defense fiscal budgets for 2024 and 2025 will be limited.。Specifically, the bill authorizes the federal government's fiscal 2024 defense and non-defense budgets to be 8,863, respectively..US $4.9 billion, 7036.$5.1 billion; authorized FY2025 defense, non-defense budget of 8952.US $1.2 billion, 7106.$8.8 billion。
In addition, the agreement increased the work requirements for receiving social benefits and announced an increase in the age of people who can receive food stamps.。The current law requires the age to apply for food relief to be 49, while the bill calls for it to be raised to 54 in order to attract more people to the workforce and save money.。Under the agreement, the job requirements for applying for cash benefits were also adjusted, but not to affect Medicaid.。
The agreement also added Republican-friendly elements, including speeding up the licensing process for energy projects.。The agreement makes the first changes to the U.S. National Environmental Policy Act in nearly 40 years, streamlining the environmental impact assessment process and making it easier for infrastructure projects to be approved, a reform that Republicans have been pushing for.。
After the agreement is reached, the market breathes a sigh of relief, and the federal government's hanging heart can be temporarily let go.。Biden called the agreement a "significant step forward" and called it a "critical project that protects working people."。"The agreement protects key priorities and legislative achievements of me and congressional Democrats, and it means that not everyone gets what they want."。"
McCarthy, for his part, said the agreement was "historic" and that it "carries out corresponding reforms to lift people out of poverty and into the labor market, and to control the government's overreach."。No new historic cuts in spending, no new government programs。"
Rebuilding coffers will significantly deplete the liquidity of the financial system The pressure on the Fed to raise interest rates in June may be reduced again.
At present, it seems that although the bill through Congress is still blocked, but overall, the bill into the voting process after the landing probability is only a matter of time, Biden and McCarthy also expressed confidence in passing the vote。What the market needs to focus on is how the macro environment will change once the bill hits the floor。
Of these, the biggest shock may be the current liquidity in the U.S. financial system.。
For the U.S. federal government, the debt ceiling was already hit on January 19 this year.。Since then, the U.S. Treasury has been taking "unconventional measures" to avoid a debt default.。According to the previous U.S. Treasury Secretary Yellen (Janet Yellen) speech, the U.S. debt default deadline was set in the coming June 5, it can be said that the U.S. government has reached the point of "out of ammunition."。
As of May 25, the Treasury's cash balance was just $38.8 billion, the lowest since 2017, up from $140 billion about half a month earlier, the data showed.。It is reported that the U.S. Treasury Department bank accounts in the short term sharp decline, precisely because of the partial avoidance of the debt ceiling was breached。
The market expects that after the debt ceiling is agreed, the U.S. Treasury's top priority will be to replenish its cash balance and ease the current "lack of money."。According to JPMorgan Chase, the U.S. Treasury could issue a total of about 1 in seven months after the debt ceiling is raised..$1 trillion national debt。And France's National Bank of Paris assessment that by the end of September this year, from bank deposits and other aspects of the flow of funds to U.S. Treasury bonds may reach about $800 billion。
In early May, the Fed had just raised the policy rate ceiling to 5.25 per cent, with a cumulative rate hike of 500 basis points over the cycle.。Under such circumstances, some banks have been overwhelmed, asset values have shrunk dramatically, deposits have continued to flow out, and finally collapsed.。At present, the credit crunch in the U.S. banking sector is a foregone conclusion, and if the U.S. Treasury drains liquidity from the financial system, it will probably only get worse: a large number of new Treasury issuance will increase the likelihood of accelerated bank outflows, and a large number of bank deposits may flow into the money fund market that invests in U.S. Treasuries and other high-yielding short-term instruments.。
In this regard, Pendal Group Ltd head of revenue strategy Patrick (Amy Xie Patrick) said that if the recent focus on issuing a large number of high-yielding government bonds, it will derive a large number of other assets in the risk of liquidity is sucked away, and further consume the size of the bank's deposits。
Bank of America also estimates that if the U.S. Treasury were to issue Treasury bills on a large scale, the impact on the economy would be equivalent to a 25 basis point rate hike by the Fed, and traders already expect the Fed to raise rates by another 25 basis points by the end of July.。

Things get a little confusing when they get here.。Originally, the two sides of the debt ceiling issue were the federal government and Congress, in which the Fed played only an "advisory" role.。In response, Fed Chairman Jerome Powell (Jerome Powell) at one point tried to avoid getting into the game.。He has said publicly that the Fed is not involved in the debt ceiling negotiations in Washington, we don't give any advice, we just remind that this issue is very important。In addition, at a closed-door meeting of House Democrats last week, Powell also insisted on avoiding talking about the U.S. debt ceiling.。
However, due to the large liquidity tightening involved in the market, the Fed may have to intervene in such a situation, at least taking the event into account in the formulation of monetary policy.。Earlier, Powell said at a monetary policy seminar that "tight credit conditions have reduced the pressure on the Fed to raise policy rates," demonstrating his willingness to constantly rethink his understanding of the current strength of monetary policy through changes in the real-time economic environment.。Separately, according to the minutes of the May FOMC meeting released last week, while members were divided on the outlook for future monetary policy, participants generally agreed on the need to closely monitor upcoming information。
Overseas, markets are also betting that Japan may allow its interest rates to rise in the next six months, which could also pose a risk of disruption to U.S. debt.。On the one hand, as the largest holder of U.S. debt, Japan's holdings of the asset has exceeded $1 trillion, and if domestic interest rates rise in Japan, capital flows will hit U.S. debt prices and raise their real yields.。On the other hand, for monetary policy, if U.S. bond yields rise, overlaid with this liquidity tightening event, the pressure on the Fed to raise interest rates will also be further reduced.。
In this case, China Merchants Macro believes that after the increase in the supply of government bonds, fiscal pressure rises, the Fed will probably increase the pressure on the banking sector and then achieve credit contraction and other ways to pressure aggregate demand, and ultimately achieve the end of interest rate hikes, turn to interest rate cuts.。
CICC said that since mid-to-early March, U.S. bond yields have fallen significantly and then remained volatile, and as a benchmark for most asset pricing, this may actually play a role in the market "spontaneous interest rate cuts," and may weaken the effect of tightening the policy itself, which may in turn delay the time for the Fed's policy to turn loose.。So on balance, the debt ceiling issue may have limited impact on the Fed's monetary policy, i.e., it is unlikely to prompt a significant shift to easing。
Overall, if the U.S. Treasury does choose to issue significant debt to rebuild its coffers, the Fed will have to take this event into account when it considers monetary policy in June for a comprehensive consideration.。But how the Fed will assess the auxiliary effect of the event on its monetary policy and its impact on inflation and the overall economy can only be glimpsed in future Fed statements.。In addition, investors will need to pay extra attention to U.S. bond yields in the near term to focus on the rest of the market's disruptions.。
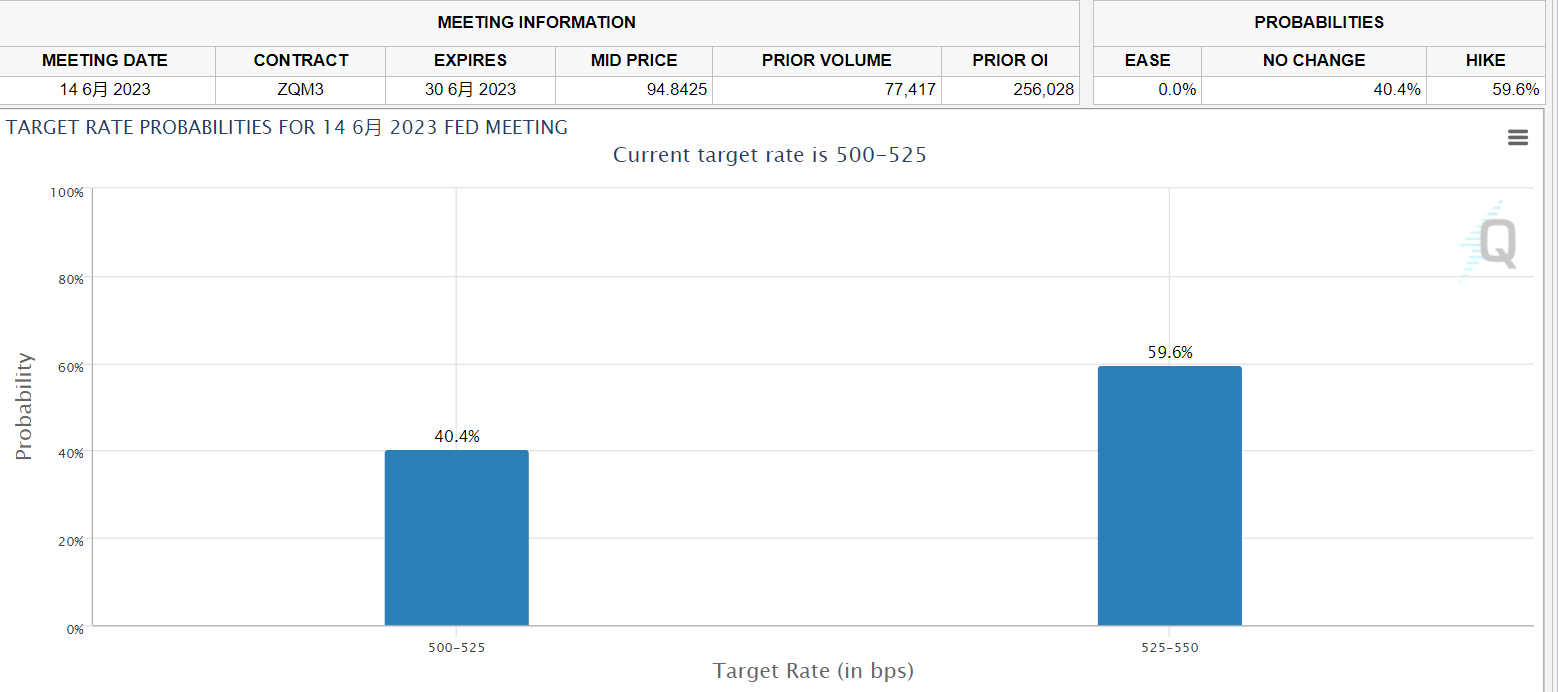
As of press time, according to CME Fed Watch, the bank's probability of suspending rate hikes in June has come to 40.4%, up from before, and the probability of another rate hike is 59.6%, down from yesterday。
Eagle Statement: This article is for reference only and does not constitute personal investment and operational advice.。Special reminder, the article is original content, without permission may not be reproduced。
·Original
Disclaimer: The views in this article are from the original Creator and do not represent the views or position of Hawk Insight. The content of the article is for reference, communication and learning only, and does not constitute investment advice. If it involves copyright issues, please contact us for deletion.